Surge protection devices (SPDs) have become essential in safeguarding electrical systems from damaging voltage spikes. With the increasing reliance on electronic devices, understanding the importance and functionality of SPDs is crucial. This comprehensive guide explores the history, advancements, and current regulations surrounding SPDs, particularly in the context of the 18th edition wiring regulations. Additionally, we’ll look at the leading brands in the market, including Fusebox, Hager, WCED, and Live, detailing their specific offerings and technical features.
The History of Surge Protection Devices
Surge protection devices were developed in response to the growing need to protect electrical equipment from voltage spikes. These spikes can be caused by various factors, such as lightning strikes, power outages, or switching operations. The earliest forms of surge protection were basic and often ineffective. However, as technology advanced, so did the sophistication of SPDs.
Early SPDs consisted mainly of simple spark gaps, which provided minimal protection. The introduction of metal oxide varistors (MOVs) in the 1970s marked a significant advancement. MOVs could absorb larger surges, offering better protection for sensitive electronic equipment. Over the years, SPDs have evolved to include features like thermal disconnects and advanced monitoring capabilities, making them more reliable and efficient.
Advancements in SPD Technology
Modern SPDs are highly effective, incorporating advanced technologies to enhance their performance. These devices now offer multi-stage protection, combining various components to provide comprehensive coverage against surges. The integration of thermal protection ensures that SPDs can disconnect safely when they overheat, preventing further damage.
Another significant advancement is the inclusion of real-time monitoring. This feature allows users to track the status of their SPDs and receive alerts if a device needs replacement. Such innovations have made SPDs more user-friendly and reliable, providing peace of mind for homeowners and businesses alike.
Moreover, the development of Type 1, Type 2, and Type 3 SPDs has revolutionized the way electrical systems are protected. Type 1 SPDs are designed to handle direct lightning strikes, making them ideal for industrial and commercial installations. Type 2 SPDs protect against residual surges from indirect strikes and switching operations, while Type 3 SPDs offer local protection for sensitive equipment.
The 18th Edition Wiring Regulations

The 18th edition wiring regulations, introduced in July 2018, have set new standards for electrical installations in the UK. These regulations emphasize the importance of surge protection, mandating the use of SPDs in certain scenarios. According to the regulations, SPDs are required in:
- Buildings where the consequences of a surge could lead to significant financial or data loss.
- Locations with large numbers of sensitive electronic devices.
- Environments where surges could impact public services or safety.
These rules aim to ensure that electrical systems are equipped to handle voltage spikes, reducing the risk of damage and enhancing overall safety.
Leading Brands and Their SPDs
1. Fusebox: Fusebox is known for its high-quality, reliable consumer units and SPDs. Established in 2017 in Kilmarnock, Scotland, Fusebox quickly gained popularity among electricians for its user-friendly designs and robust performance. Their SPDs are designed to offer maximum protection with minimal maintenance. Features include:
- Compact design for easy installation.
- Integrated thermal protection.
- Real-time status indicators.
Fusebox’s SPDs are designed with the end-user in mind, ensuring that even those with limited technical knowledge can easily understand and maintain their devices. Their products are also known for their affordability without compromising on quality, making them a popular choice for both residential and commercial installations.
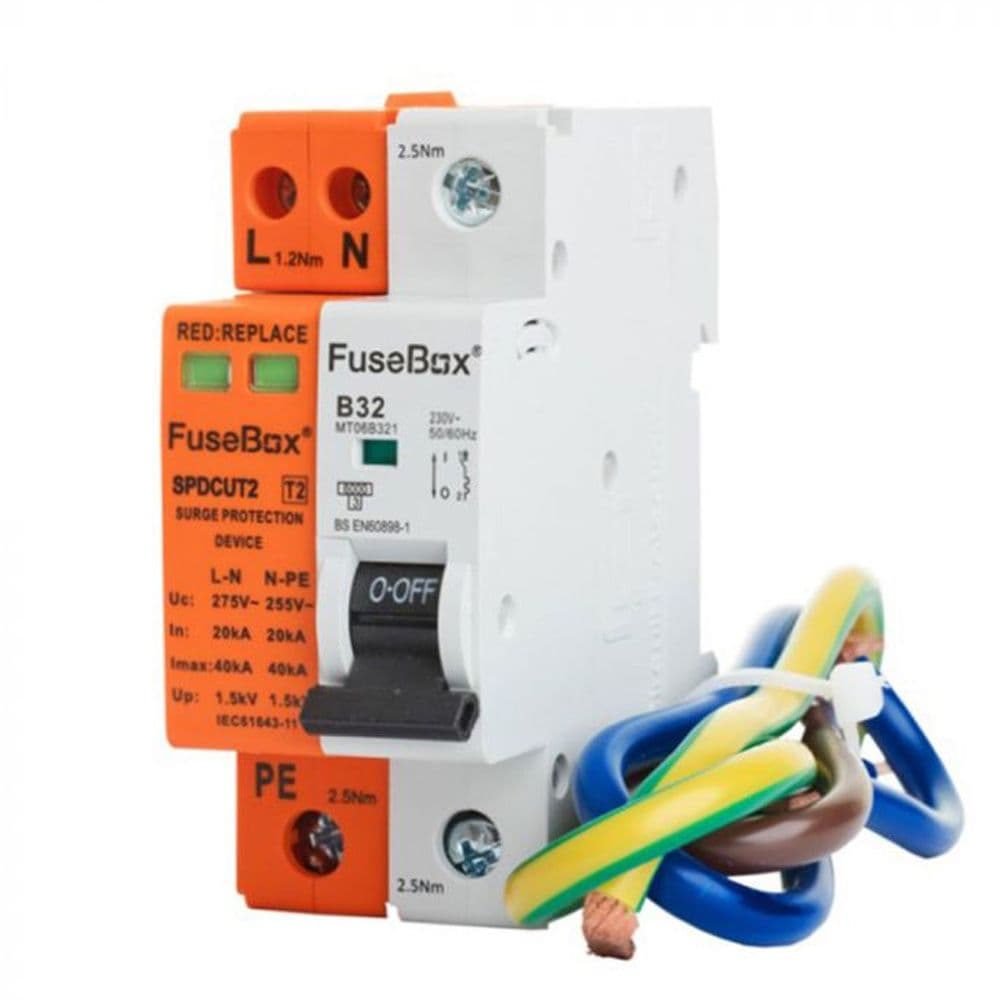

2. Hager: Hager is a well-established name in the electrical industry, offering a wide range of SPDs. Known for their innovative designs and durability, Hager SPDs are suitable for both residential and commercial applications. Technical details include:
- Type 1, Type 2, and combined Type 1+2 SPDs.
- Advanced thermal disconnect mechanisms.
- High energy absorption capacity.
Hager’s SPDs are designed to meet the highest safety standards, ensuring reliable protection for electrical systems. The company’s focus on innovation has led to the development of SPDs that are not only effective but also easy to install and maintain. Hager’s commitment to quality and customer satisfaction makes them a trusted choice for electricians and homeowners alike.

3. WCED: WCED provides robust and reliable SPDs designed for various applications. Their products are renowned for their ease of installation and high performance. Key features include:
- Modular design for flexibility.
- High surge capacity.
- Compliance with the latest safety standards.
WCED’s SPDs are built to withstand the harshest conditions, providing reliable protection for electrical systems. The company’s focus on flexibility means that their SPDs can be easily integrated into existing systems, making them a convenient choice for both new installations and upgrades. WCED’s commitment to safety and performance ensures that their products are trusted by professionals worldwide.

4. Live: Live Electric is another reputable brand offering a range of SPDs known for their efficiency and reliability. Their products are designed to provide comprehensive protection for electrical systems, ensuring long-term safety and performance. Highlights include:
- Multi-stage protection.
- Compact and durable construction.
- Easy integration with existing systems.
Live Electric’s SPDs are designed to offer maximum protection with minimal maintenance, making them an ideal choice for both residential and commercial installations. The company’s focus on durability ensures that their products can withstand the rigors of everyday use, providing reliable protection for years to come. Live Electric’s commitment to innovation and customer satisfaction makes them a trusted name in the industry.
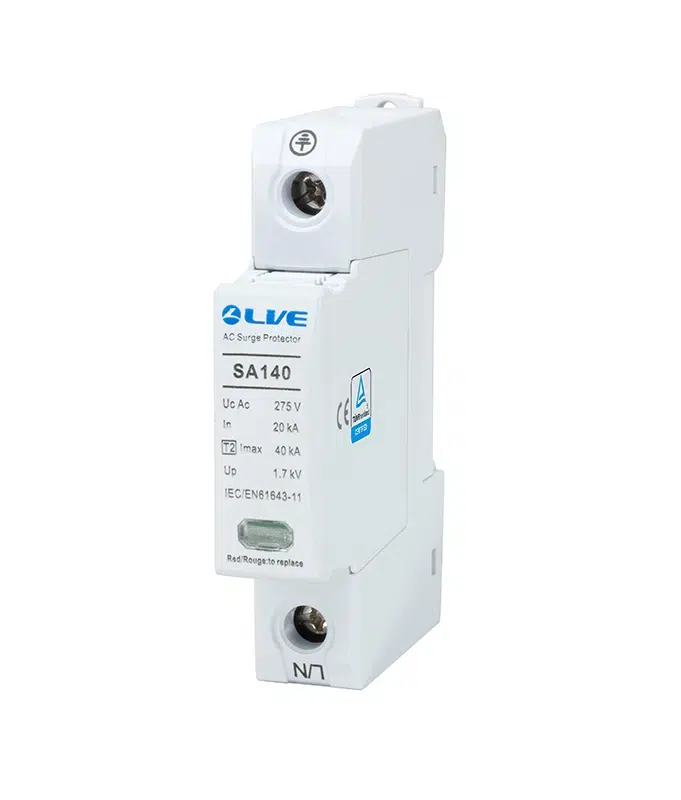

Technical Details of SPDs
SPDs are classified into different types based on their application and protection levels:
- Type 1 SPDs: Installed at the origin of the electrical system, typically in commercial and industrial settings. They protect against direct lightning strikes.
- Type 2 SPDs: Installed at distribution boards, providing protection against residual surges from indirect lightning strikes and switching operations.
- Type 3 SPDs: Used for local protection of sensitive equipment, typically installed close to the device.
Type 1 SPDs are designed to handle the highest levels of surge energy, making them ideal for protecting critical infrastructure. Type 2 SPDs provide a secondary level of protection, ensuring that any residual surge energy is safely diverted away from sensitive equipment. Type 3 SPDs offer additional protection for specific devices, ensuring that even the most sensitive electronics are safeguarded against voltage spikes.
Installation and Maintenance of SPDs
Proper installation and maintenance of SPDs are crucial for ensuring their effectiveness. SPDs should be installed by qualified professionals, following the manufacturer’s guidelines and the requirements of the 18th edition wiring regulations. Regular inspections and maintenance are also essential to ensure that SPDs are functioning correctly and providing the necessary protection.
During installation, it is important to ensure that SPDs are connected in parallel with the electrical system, allowing them to divert excess voltage to the ground. This setup ensures that SPDs can protect the entire system without interfering with normal operations. Additionally, SPDs should be installed as close to the protected equipment as possible, minimizing the distance that surge energy must travel.
Regular maintenance of SPDs involves checking for signs of damage or wear, ensuring that all connections are secure, and replacing any devices that have been compromised by previous surges. Many modern SPDs include status indicators that provide real-time information about the device’s condition, making it easier to identify when maintenance is needed.
Conclusion
Surge protection devices are essential for safeguarding electrical systems from damaging voltage spikes. The advancements in SPD technology, combined with stringent regulations like the 18th edition wiring regulations, ensure that modern electrical systems are well-protected. Brands like Fusebox, Hager, WCED, and Live offer a range of high-quality SPDs, catering to various needs and applications. Understanding the importance of SPDs and choosing the right one for your specific needs can protect your equipment and enhance overall safety.
A surge protection device protects electrical equipment from voltage spikes by diverting excess voltage to the ground, preventing damage.
Yes, surge protectors are essential to protect sensitive electronic devices from power surges, as mandated by the 18th edition wiring regulations.
SPDs should be installed at the main distribution board and close to sensitive equipment to provide comprehensive protection.
Yes, according to the 18th edition wiring regulations, SPDs are required in certain scenarios to ensure electrical safety.
If your building houses sensitive electronic equipment or if surges could lead to significant loss or safety issues, you need surge protection.
Surge protectors should be used in all electrical installations, especially in environments with sensitive electronics or where surges could cause significant damage.
SPDs should be installed during the initial electrical installation or when upgrading an existing system to comply with the 18th edition wiring regulations.
Yes, installing SPDs in your house protects your appliances and electronics from voltage spikes, enhancing safety and longevity.
Yes, homes with sensitive electronic devices should have surge protection to prevent damage from electrical surges.
Yes, the absence of required SPDs can result in a failed Electrical Installation Condition Report (EICR), as per the 18th edition regulations. (In some scenarios)
SPDs should be installed at the main distribution board and as close to sensitive equipment as possible for optimal protection.
The 18th edition wiring regulations, introduced in 2018, set safety standards for electrical installations, including the requirement for SPDs.
SPDs should be installed on the incoming side of the mains switchboard to provide protection for the entire electrical system.
The 10m rule states that SPDs should be installed within 10 meters of the equipment they are protecting to ensure effective surge protection.
An MCB can be used to protect the SPD circuit, ensuring that any faults do not affect the entire electrical system.
SPDs should be installed before RCDs to ensure that they can protect the entire electrical system from surges.
SPDs do not have to be next to the main switch, but they should be installed as close as possible to the main distribution board.
SPDs are connected in parallel with the electrical system, allowing them to divert excess voltage to the ground without interrupting normal operations.
SPDs are wired in parallel with the electrical system, with connections to the live, neutral, and ground wires.
SPDs can be installed at the main distribution board, sub-panels, or close to sensitive equipment to provide comprehensive protection.
SPD protection is necessary in buildings with sensitive electronic equipment, where surges could cause significant damage or safety issues.
Type 1 SPDs protect against direct lightning strikes, while Type 2 SPDs protect against residual surges from indirect strikes and switching operations.
Type 1 SPDs are needed for buildings with external lightning protection, while Type 2 SPDs are suitable for most residential and commercial applications.
Choose an SPD based on your specific needs, considering factors like the type of protection required, surge capacity, and installation environment.
Yes, combining surge protection with RCBOs ensures comprehensive protection against both surges and overloads or short circuits.
No, MCBs protect against overloads and short circuits but do not provide surge protection. SPDs are required for surge protection.
RCBOs provide combined protection against overloads, short circuits, and earth faults, offering more comprehensive protection than RCDs alone.
No, RCDs protect against earth faults but do not provide surge protection. SPDs are necessary for protecting against voltage spikes.
SPDs are required in buildings with sensitive electronic equipment or where surges could lead to significant loss or safety issues.
Appliances with sensitive electronic components, such as computers, TVs, and home entertainment systems, should be protected by surge protection devices.
- ⚡ Surge Devices: The Ultimate Guide to Surge Protection Devices (SPD)
- 🔥 Modifying Consumer Units: Why “It Fits” Can Still Fail
- 🏡 Consumer Units in New Builds: Why Boards Are Now Out in the Open
- Amendment 4 and Consumer Units
- Henley Blocks Reimagined: From Industrial Roots to Colour-Coded 100A Connectors